In today’s digital age, mobile hotspots have become indispensable tools for many. Whether you’re working remotely, traveling, or simply needing an internet connection on the go, hotspots are there to save the day. But have you ever wondered how much data a hotspot uses? Let’s delve deep into this topic and shed light on all the intricacies of hotspot data usage.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
The ability to create a mobile hotspot and share your device’s internet connection with others is nothing short of revolutionary. It’s a lifeline in areas with no Wi-Fi, and, for many, a daily necessity. However, with great power comes great responsibility; understanding your hotspot’s data consumption is crucial to avoid unexpected charges and ensure seamless connectivity.
1. What is a Mobile Hotspot?
A mobile hotspot, often simply referred to as a “hotspot,” is a portable device or a feature available on many modern smartphones and tablets that allows you to share your device’s cellular data connection with other devices. This essentially transforms your device into a mini Wi-Fi router, providing internet access to any device connected to it.
- The Mechanics of a Mobile Hotspot:
- When you activate the hotspot feature, your device creates a wireless local area network (WLAN). This network provides internet access by leveraging your device’s cellular connection.
- Devices such as laptops, tablets, other smartphones, and even gaming consoles can connect to this network, much like they would to any other Wi-Fi network.
- Tethering vs. Hotspot:
- While the terms “tethering” and “hotspot” are often used interchangeably, they are slightly different. Tethering typically refers to a direct connection between two devices, often using a USB cable. A hotspot, on the other hand, provides wireless internet access to multiple devices.
- Dedicated Hotspot Devices:
- Apart from the hotspot feature on smartphones and tablets, there are dedicated mobile hotspot devices, often called “Mi-Fi” or “pocket routers.” These are standalone devices that connect to a cellular network and broadcast a Wi-Fi signal, allowing multiple devices to connect and access the internet.
- Such devices are especially useful for those who frequently travel or require a backup internet source. They often come with more advanced features, such as longer battery life, stronger signal strength, and the ability to connect more devices simultaneously.
- Data Plans and Hotspots:
- Using a mobile hotspot consumes data from your cellular plan. It’s essential to be aware of your data limits, especially if multiple devices are connected and performing high-bandwidth activities.
- Some cellular plans offer dedicated hotspot data, separate from regular data usage. It’s crucial to check with your service provider about the specifics of your plan.
- Security Considerations:
- Just like any other Wi-Fi network, it’s vital to secure your mobile hotspot. Ensure you have a strong password to prevent unauthorized access. Most devices also allow you to hide the network name (SSID) for added security.
- Regularly updating the device’s firmware and changing passwords can further enhance security.
By understanding the nuances and capabilities of mobile hotspots, users can make informed decisions about when and how to use this powerful feature, ensuring efficient and secure internet access on the go.
2. Factors Influencing Hotspot Data Usage
Understanding how much data a hotspot uses is not as straightforward as it might seem. Several variables come into play, each influencing the overall data consumption. Let’s delve deeper into these factors to get a clearer picture of how hotspot data usage is determined.
- 2.1 Device Connections
- Number of Devices: The more devices you have connected to your hotspot, the higher the overall data consumption. Each device, whether it’s a smartphone, tablet, or laptop, will pull data from the hotspot, leading to increased usage.
- Types of Devices: Different devices have different data consumption patterns. For instance, a laptop updating its software or streaming high-definition videos will typically use more data than a smartphone browsing social media.
- 2.2 Type of Activities
- Browsing vs. Streaming vs. Gaming: The kind of online activity significantly impacts data usage. For example, reading articles or checking emails is relatively light on data. In contrast, streaming videos, especially in high-definition, or playing online multiplayer games can consume data rapidly.
- HD vs. SD Streaming: Streaming content in high-definition (HD) can use up to three times more data than standard-definition (SD). It’s essential to be aware of the streaming quality settings on platforms like Netflix or YouTube.
- Background Activities: Even if you’re not actively using a device, it might still consume data in the background. This can include app updates, cloud backups, and automatic synchronization of data.
- 2.3 Background Applications
- Updates and Syncs: Many devices, especially laptops, have applications that automatically update in the background. These updates can sometimes be large and significantly impact data usage. Similarly, services like Dropbox or Google Drive might sync files in the background.
- Cloud Backups: Devices connected to the hotspot might be set to backup photos, videos, or other data to cloud services automatically. This process, especially if there are large files involved, can consume a significant amount of data.
- 2.4 Duration of Connection
- The longer devices are connected to a hotspot, the more data they’re likely to use. It’s not just about the intensity of the activity but also the duration. For instance, streaming a movie for two hours will naturally use more data than streaming for just thirty minutes.
- 2.5 Quality of Cellular Connection
- The speed and quality of your cellular connection can also influence data consumption. A faster 4G or 5G connection might lead to websites loading more quickly, apps updating faster, and videos streaming at higher quality, all of which can increase data usage.
- 2.6 Automatic Settings and Optimizations
- Some devices and apps have built-in optimizations to reduce data usage when connected to a hotspot. For instance, smartphones might switch to a “data saver” mode, and certain apps might reduce the quality of streaming or downloads to conserve data.
By being aware of these factors and actively managing them, users can have better control over their hotspot’s data consumption, ensuring they get the most out of their available data without any unexpected overages.
3. Average Data Consumption for Common Activities
The amount of data consumed during hotspot usage can vary widely based on the specific activities being performed. To provide a clearer understanding, let’s break down the average data consumption for some of the most common online activities.
- 3.1 Browsing the Web
- General Browsing: On average, general web browsing, which includes visiting websites, reading articles, and checking emails, uses about 50–70 MB of data per hour. However, this can vary based on the complexity of the websites and the number of images or multimedia elements they contain.
- Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, which are rich in multimedia content, can consume anywhere from 150MB to 200MB per hour, depending on the frequency of video playback and image loading.
- 3.2 Streaming Videos
- YouTube: Streaming videos on YouTube can vary widely in data consumption. On average, watching in standard definition (SD) uses approximately 250MB per hour, while watching in high definition (HD) can consume up to 1.5GB per hour.
- Netflix: Streaming on platforms like Netflix has a broader range due to the availability of different quality settings. Roughly, SD streaming uses about 1GB per hour, HD uses around 3GB, and ultra-high-definition (4K) can consume up to 7GB per hour.
- 3.3 Online Gaming
- Contrary to popular belief, most online games don’t consume as much data as streaming videos. On average, online games use between 40 and 150MB per hour. However, this figure can vary based on the game’s complexity, real-time updates, and in-game downloads.
- Game Downloads and Updates: While playing might not consume much data, downloading new games or updates can be data-intensive, sometimes requiring several gigabytes of data.
- 3.4 Video Calls
- Platforms like Zoom, Skype, or Microsoft Teams have become essential for work and personal communication. Data consumption here depends on the video quality and the number of participants. On average:
- One-on-One Calls: Around 270MB to 540MB per hour.
- Group Calls: Can go up to 1GB or more per hour, especially with multiple video feeds.
- Platforms like Zoom, Skype, or Microsoft Teams have become essential for work and personal communication. Data consumption here depends on the video quality and the number of participants. On average:
- 3.5 Music Streaming
- Listening to music on platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, or Pandora typically consumes about 40MB to 150MB per hour, depending on the audio quality settings.
- 3.6 Downloads and Uploads
- Downloading or uploading files, be they documents, images, or software, directly impacts data usage. A single high-resolution image can be 5MB, a song can be around 4MB, and software updates can range from a few megabytes to several gigabytes.
- 3.7 Cloud Services
- Activities like auto-syncing photos to the cloud, backing up data, or accessing files from cloud storage can also consume significant data. The exact amount depends on the size and type of files being transferred.
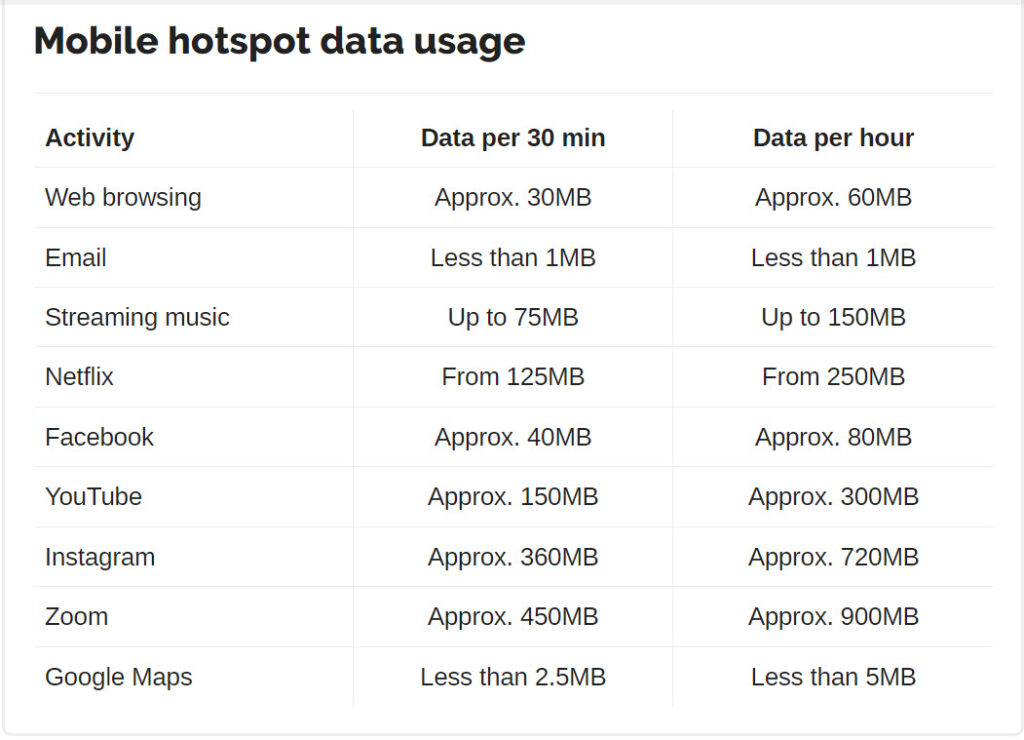
Understanding the average data consumption for these activities can help users make informed decisions about their hotspot usage, ensuring they can manage their data effectively and avoid unexpected overages.
4. Tips to Monitor and Reduce Hotspot Data Usage
As reliance on mobile hotspots grows, it becomes increasingly important to monitor and manage data consumption effectively. Here are some practical tips and strategies to help users keep track of their hotspot data usage and implement measures to reduce unnecessary consumption.
- 4.1 Monitor Data Usage Regularly
- Built-in Device Features: Most smartphones and tablets have built-in features that allow users to monitor their data usage. Navigate to the device’s settings to view a breakdown of data consumption by individual apps and services.
- Carrier Apps: Many cellular service providers offer dedicated apps that provide real-time data usage statistics, set alerts, and even purchase additional data if needed.
- 4.2 Set Data Limits and Alerts
- Users can set data limits on their devices, ensuring they don’t exceed their data allowance. Once the set limit is reached, the device will automatically disable mobile data or send an alert.
- Setting periodic alerts (e.g., when 50% or 75% of data is consumed) can also help users stay informed and adjust their usage patterns accordingly.
- 4.3 Limit High-Data Activities
- Consider postponing activities that consume large amounts of data, such as software updates, large downloads, or HD video streaming, until you have access to a Wi-Fi network.
- Opt for lower-quality streaming. For instance, switch from HD to SD video or reduce the audio quality on music streaming apps.
- 4.4 Restrict Background Data
- Many apps continue to use data in the background, even when they’re not actively in use. By restricting background data for non-essential apps, users can significantly reduce unintended data consumption.
- This can be done through the device’s settings, where users can choose which apps can use data in the background.
- 4.5 Use Data-Saving Modes
- Many browsers and apps offer a “data-saving” or “lite” mode, which reduces the amount of data used by compressing images, videos, and other elements.
- Platforms like Google Chrome and YouTube have these features, which can be activated through their settings.
- 4.6 Secure Your Hotspot
- Ensure your mobile hotspot is password-protected to prevent unauthorized access. Unwanted connections can quickly consume your data allowance without your knowledge.
- 4.7 Regularly Update Apps and Software
- Keeping apps and software updated can sometimes lead to better data optimization. Developers often release updates that make apps more efficient and less data-intensive.
- 4.8 Optimize Cloud Settings
- If you use cloud services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or iCloud, ensure they’re not set to automatically backup large files or sync when connected to your hotspot. Adjust the settings to manual syncing or backup to control data usage.
- 4.9 Consider an Unlimited Data Plan
- If you frequently rely on your hotspot and find yourself consistently exceeding your data limits, it might be worth considering a plan with unlimited data or a higher data allowance.
By implementing these tips and being proactive in monitoring data usage, users can make the most of their mobile hotspot while avoiding unexpected charges and ensuring a smooth online experience.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Mobile hotspots are incredibly useful, but they can also lead to a plethora of questions, especially for those new to the concept. Here’s a deeper dive into some of the most frequently asked questions about hotspot data usage.
- 5.1 How is hotspot data different from mobile data?
- While both hotspot data and mobile data draw from the same source (your cellular data plan), they serve different purposes. Mobile data is what your phone uses for its own internet activities, like browsing or using apps. Hotspot data, on the other hand, is the data used by other devices connected to your phone’s hotspot feature.
- 5.2 Can I use a hotspot without using data?
- No, the primary function of a hotspot is to share your device’s cellular data connection with other devices. Therefore, any activity on devices connected to the hotspot will consume data.
- 5.3 Why is my hotspot data usage higher than my device’s usage?
- The data consumption on a hotspot can be higher because multiple devices might be connected, each with its own set of activities. For instance, one device might be streaming a movie while another is downloading a large file, leading to higher combined data usage.
- 5.4 How can I check which device is using the most data on my hotspot?
- Some hotspot devices and carrier apps provide detailed breakdowns of data usage by connected devices. If your device or app doesn’t offer this feature, consider third-party apps or software that can monitor data usage on connected devices.
- 5.5 Is there a way to prioritize data usage for specific devices connected to my hotspot?
- Some advanced mobile hotspot devices allow for Quality of Service (QoS) settings, where you can prioritize data for specific devices or activities. This ensures that essential tasks get the bandwidth they need.
- 5.6 Can using a VPN on a device connected to my hotspot reduce data usage?
- While VPNs can provide security and privacy, they don’t inherently reduce data usage. In fact, due to encryption, using a VPN might slightly increase the amount of data used. However, some VPN services offer data compression features that can help reduce data consumption.
- 5.7 Does turning off video auto-play on apps reduce hotspot data usage?
- Yes, turning off auto-play, especially for videos on platforms like Facebook or Instagram, can significantly reduce data usage. Videos can consume a large amount of data, and preventing them from playing automatically can lead to noticeable savings.
- 5.8 What happens if I exceed my hotspot data limit?
- This depends on your carrier and plan. Some carriers might reduce the speed (throttle) of your hotspot connection after reaching the data limit, while others might charge overage fees. It’s essential to be aware of your plan’s specifics to avoid unexpected charges or reduced speeds.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, users can gain a clearer understanding of how hotspots function and how to manage their data usage effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding your hotspot’s data usage is more than just a numbers game; it’s about optimizing your connectivity experience. By staying informed and proactive, you can make the most of your mobile hotspot without any unexpected surprises.
Call to Action (CTA)
Found this guide helpful? Share your experiences or additional tips in the comments below. We’d love to hear from you!

