Imagine a world where traffic jams are a thing of the past, where your car drives you safely while you catch up on work or relax with a book. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the rapidly approaching future of transportation, led by innovations like autonomous vehicles or self-driving cars. This blog explores the incredible possibilities and the challenges that come with driverless technology, while also delving into other exciting advancements in how we get around. Welcome to a journey into the future!
The Dawn of Driverless: Understanding Autonomous Vehicles
Let’s start with the star of the show: autonomous vehicles, often called self-driving cars. These are vehicles that can operate without human input. Think of it like your car having its own super-skilled driver, powered by advanced technology. But it’s not just about skipping the commute; it’s a revolution in how we move, live, and interact with the world around us.
What Makes a Car ‘Self-Driving’?
It’s not magic; it’s a combination of sophisticated systems working together:
- Sensors: These are the car’s ‘eyes and ears’, including cameras, radar, lidar, and ultrasonic sensors. They constantly scan the environment to understand its surroundings – other vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signs, and road markings.
- AI (Artificial Intelligence): This is the ‘brain’ of the operation. AI algorithms process the data from the sensors, allowing the car to make informed decisions on everything from navigating intersections to avoiding collisions. The role of AI in autonomous cars is critical for learning, adapting, and improving driving performance over time.
- Mapping Systems: High-definition maps, constantly updated, help the car know where it is, what roads are like, and what the optimal route might be.

Levels of Automation: Not All Self-Driving Cars Are Created Equal
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of driving automation, from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation):
- Level 0: No Automation: The driver is fully responsible for all driving tasks (most cars today).
- Level 1: Driver Assistance: The car can help with one driving task, like cruise control or lane assist.
- Level 2: Partial Automation: The car can control steering and acceleration/deceleration, but the driver still needs to be alert and ready to take over.
- Level 3: Conditional Automation: The car can manage most driving tasks in certain situations, but the driver must be ready to intervene if needed.
- Level 4: High Automation: The car can handle most driving situations in a specific location and circumstance, like in a designated ‘geo-fenced’ area, without driver input.
- Level 5: Full Automation: The car can drive anywhere, anytime, under all conditions, without human intervention, just like in our sci-fi dreams.
Currently, we mostly see cars at Level 2, with some starting to push into Level 3. The goal, of course, is to reach Level 5, which would truly revolutionize personal transport.
The Benefits: Why Are Self-Driving Cars So Exciting?
The potential upsides of autonomous vehicles are vast and transformative:
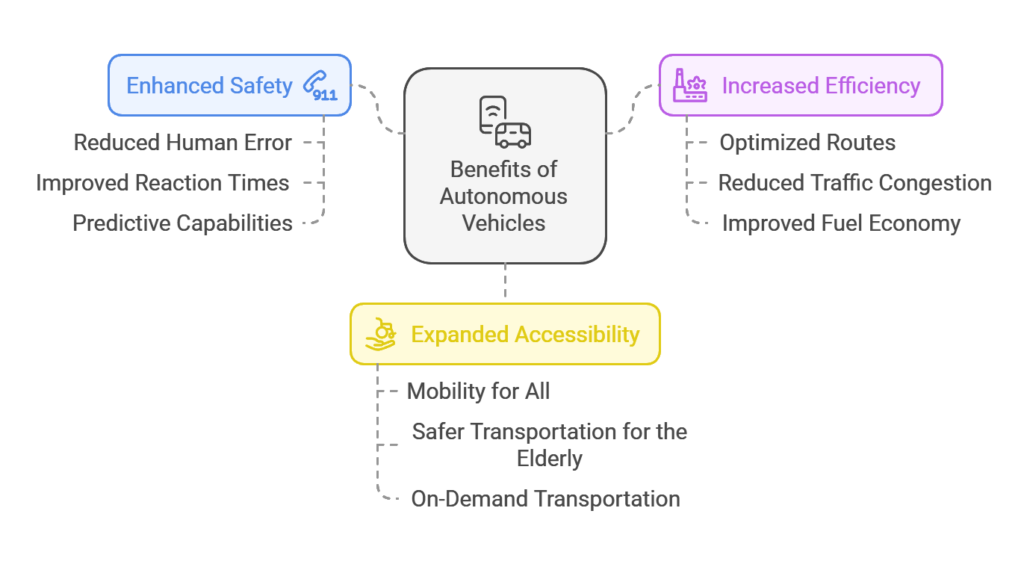
- Improved Safety: This is the biggest draw. Most accidents are caused by human error. Driverless technology, by removing human fallibility (like distracted driving or driving under the influence), could dramatically reduce accidents. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), 94% of accidents are caused by human error. This is a compelling statistic for the need for autonomous driving.
- Increased Mobility: Self-driving cars can provide independence to those who can’t drive due to age or disability. Imagine the elderly being able to go anywhere without relying on others – this is a massive improvement in their quality of life.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: Autonomous vehicles, connected to smart transportation systems, can optimize traffic flow, reducing gridlock and making commutes faster and less stressful. AI systems learn through collected data how to best navigate various road conditions and traffic patterns.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: By driving more smoothly and consistently, autonomous cars can optimize fuel consumption and reduce emissions. This will be very beneficial as we transition to more electric vehicle use in the future of transportation.
- Increased Productivity: Commuters can work, relax, read, or do other things while being chauffeured, effectively turning travel time into productive time.
- Efficient Logistics: Autonomous trucks can help optimize shipping, leading to faster and more efficient delivery of goods, reducing logistics costs.
The Challenges: Roadblocks to Autonomous Vehicle Adoption
The journey to widespread adoption of self-driving cars is not without its hurdles. Some of the key challenges of self-driving cars include:
- Technological Hurdles: Ensuring that the technology is reliable and can handle all driving scenarios, including unexpected events, adverse weather, or complex traffic situations. The need for constant software updates and robust AI is crucial.
- Regulatory and Legal Frameworks: Establishing clear legal guidelines about liability in case of accidents. These rules are not yet clear across states and countries and this needs to be settled before fully autonomous vehicles can safely be released into the general population.
- Public Acceptance: Building public trust in the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles. Many people are initially hesitant to let a machine handle all driving tasks.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Ensuring our roads and infrastructure are ready to support self-driving cars, including high-definition mapping, charging stations, and communication networks.
- Ethical Dilemmas: How should an autonomous car respond in unavoidable accident scenarios? Who is liable for an accident? The answers to these ethical questions need careful consideration.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting these complex systems from hacking, as a breach could have serious safety consequences.
Beyond Self-Driving Cars: A Broader Look at Transportation Innovation
The future of transportation goes far beyond just self-driving cars. It’s a mosaic of exciting innovations:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): The shift towards electric vehicles is critical for sustainable mobility solutions, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Electric autonomous vehicles combine the best of both worlds, making transportation not only smart but also eco-friendly.
- Connected Car Technology: Vehicles will be increasingly interconnected with each other and their surroundings, sharing data and information to enhance safety and optimize traffic flow. Think of it like a smart, communicative network of cars. This can include technologies such as vehicle-to-vehicle communication (V2V), vehicle-to-infrastructure communication (V2I), and vehicle-to-everything communication (V2X).
- Smart Transportation Systems: Cities are developing integrated systems that use data and technology to optimize public transportation, traffic management, parking, and even bicycle networks.
- High-Speed Rail: Innovations in high-speed rail offer a faster and more sustainable alternative to air travel and long-distance road trips.
- Hyperloop Technology: This futuristic technology involves traveling in pods through low-pressure tubes, with the promise of extremely fast long-distance transport.
- Drones and Air Taxis: These could potentially revolutionize urban mobility and goods delivery, offering new options in congested cities and remote areas. Emerging transportation technologies like these are rapidly making headway.

AI in Transportation: The Engine of Progress
AI in transportation isn’t just about self-driving cars. It permeates nearly every aspect of modern transit:
- Route Optimization: AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to find the most efficient routes, minimizing traffic congestion and travel times.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze vehicle data to identify potential problems before they become major issues, reducing downtime and improving safety.
- Personalized Travel Experiences: AI can be used to create personalized travel recommendations based on preferences, schedule, and real-time conditions.
- Public Transportation Optimization: AI helps to improve the efficiency of public transport networks by analyzing data on ridership and optimizing routes and schedules.
The Path Forward: Embracing the Future of Mobility
The future of transportation is rapidly evolving, and we’re at a crucial point where these technologies are moving from the realm of science fiction to reality. To ensure a smooth and beneficial transition, we must:
- Invest in Research and Development: Continue to explore and develop innovative transportation technologies.
- Establish Clear Regulations: Create clear legal and regulatory frameworks to guide the development and deployment of these technologies, ensuring safety and addressing ethical concerns.
- Invest in Infrastructure: Build the necessary infrastructure to support new transportation technologies like charging stations, updated roads, and communication networks.
- Educate the Public: Improve public awareness and understanding of the benefits and limitations of new transportation technologies.
- Collaborate: Bring together stakeholders from government, industry, and academia to create a shared vision for the future of transportation.
Conclusion: A Transformative Journey
The transition to autonomous vehicles and other emerging transportation technologies will not be without its challenges. However, the potential benefits – safer roads, more efficient transportation, and greater accessibility – are enormous. By embracing transportation innovation and addressing the challenges proactively, we can create a future where moving around is safer, more sustainable, and more enjoyable for everyone. The road ahead is exciting, and we’re all in for the ride. What role do you see yourself playing in this futuristic landscape? Let us know in the comments!

