1. What is the Dark Web? Peeling Back the Layers of the Hidden Internet
The internet. It’s a vast, sprawling landscape, a digital ocean teeming with information. We all navigate it daily, clicking through websites, scrolling through social feeds, and searching for answers on Google. But what if I told you that what you see every day is just the tip of the iceberg? Beneath the surface lies a hidden world, often shrouded in mystery and misunderstanding: the Dark Web.
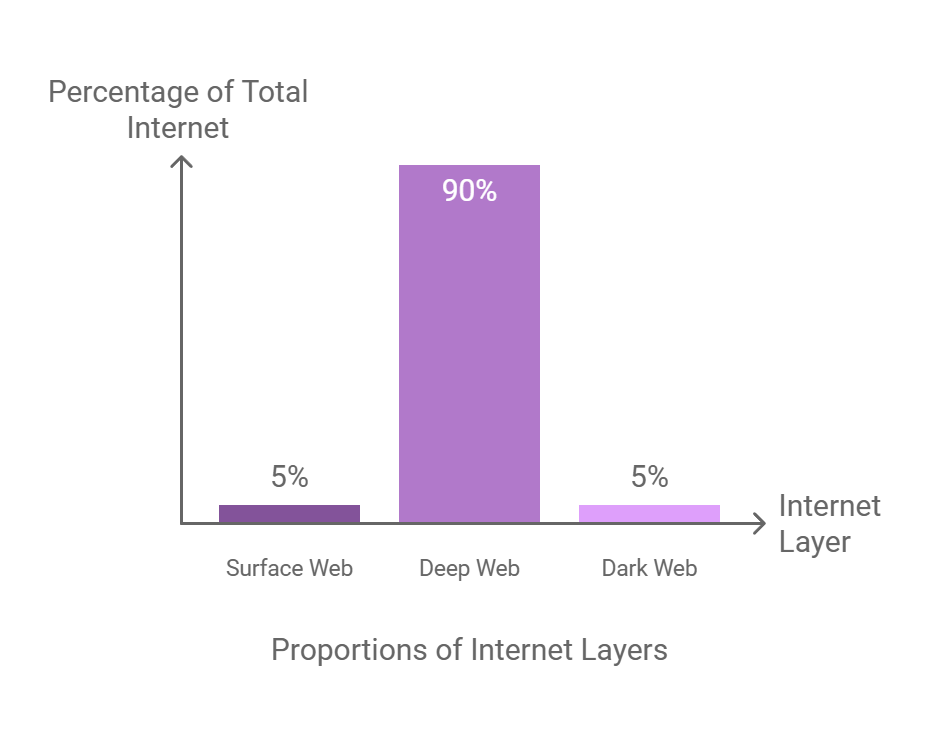
So, what is the Dark Web exactly? To understand it, we need to think of the internet in layers. Imagine an iceberg. The part we see above the water, the surface, is the “Surface Web.” This is where all the websites you access through search engines like Google and Bing live. These sites are indexed, meaning search engines can find and catalog them.
Below the surface lies the “Deep Web.” This area includes content that isn’t indexed by search engines, like your online banking portal, email accounts, cloud storage, and academic databases. It’s a massive part of the internet, far larger than the Surface Web, and it’s completely legitimate.
Finally, at the very bottom, the mysterious and often maligned part, lies the Dark Web. The Dark Web is a small subsection of the Deep Web that requires specialized software, such as the Tor browser, to access. It’s a network of anonymized websites, often using the “.onion” domain extension. This anonymity is what gives the Dark Web its infamous reputation, and as we’ll explore further, it’s both a source of good and bad.
Think of it this way, the Dark Web is not some shadowy parallel internet. It’s part of the same internet infrastructure we all use, but it’s accessed in a way that makes it harder to track, control, and find using normal web tools. While often associated with nefarious activities, the Dark Web also has legitimate uses. It provides a secure platform for journalists and whistleblowers to communicate without fear of censorship, activists to organize in oppressive regimes, and everyday citizens seeking privacy.
2. Dark Web vs Deep Web: Clearing the Confusion – The Difference Between What’s Hidden and What’s Truly Obscure
One of the biggest sources of confusion for those new to the topic is the difference between the Deep Web and the Dark Web. It’s understandable! Both deal with content hidden from the Surface Web, but they are distinct entities with very different functions. So, let’s break down the key differences:
As we established earlier, the Deep Web includes everything not indexed by search engines. Think of it as the “unlisted” areas of the internet. This includes:
- Private databases: Like student portals, medical records, or corporate databases.
- Subscription-based content: Like paywalled articles, online courses, and streaming services.
- Personal cloud storage: Your Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive folders.
- Intranets: Internal networks used by companies and organizations.
The Dark Web, on the other hand, is a smaller, anonymized segment of the Deep Web. Here are the key features:
- Accessibility: Requires specialized software like Tor to access. Standard browsers won’t work.
- Anonymity: Uses encryption techniques to mask the location and identity of both users and website hosts.
- Content: Is not easily searchable, making the information harder to find.
- Purpose: Primarily used for increased privacy, security, and anonymity, but also harbors illegal marketplaces and activities.
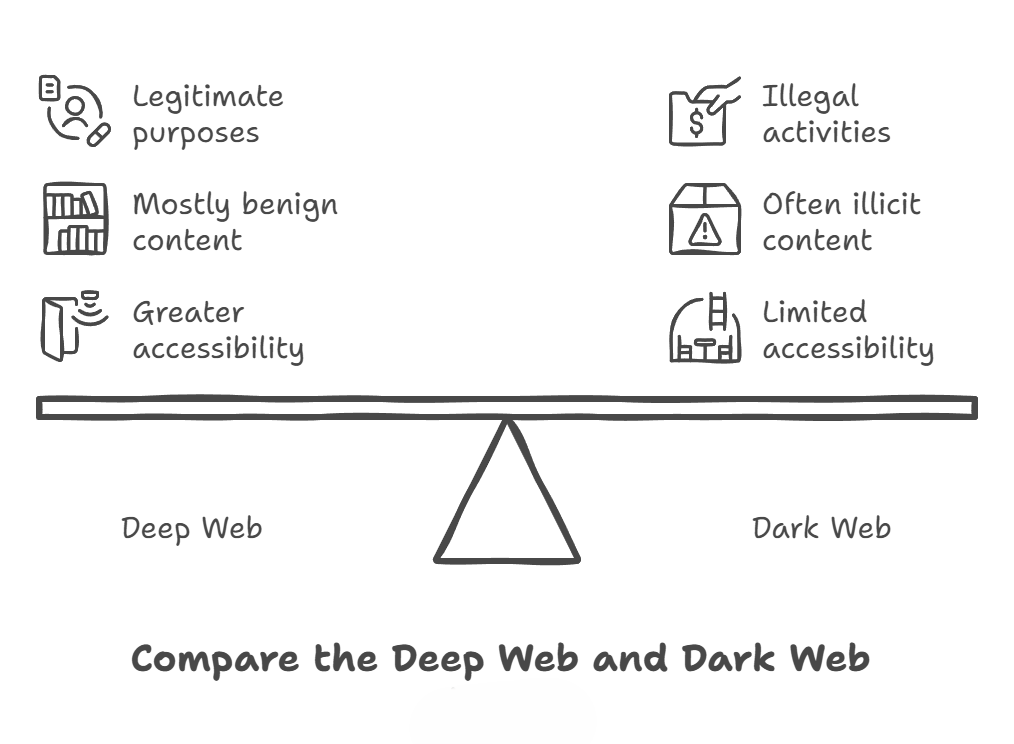
It’s important to remember the scale: the Deep Web is massive, encompassing most of the internet’s content, while the Dark Web is a very small portion of the Deep Web, specifically designed to be hidden. The Dark Web vs Deep Web distinction is crucial; not everything hidden is illegal or dangerous, but the specific focus on anonymity makes the Dark Web a breeding ground for less regulated content.
3. How to Access the Dark Web Safely: Navigating the Shadows with Caution
The intrigue surrounding the Dark Web often leads to a desire to explore it. However, before you dive in, it’s crucial to understand how to access it safely and responsibly. This isn’t like browsing Facebook or doing online shopping; accessing the Dark Web requires specific tools and a cautious mindset.
The most common tool for accessing the Dark Web is the Tor Browser. Tor (The Onion Router) is a free, open-source software that routes your internet traffic through a series of encrypted relays, making it very difficult to trace your activity. Download it from the official Tor Project website to avoid tampered versions.
Beyond Tor, consider using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) in conjunction. A VPN encrypts your internet connection and routes your traffic through a server in a location of your choosing, adding another layer of anonymity. Using a VPN in conjunction with Tor further reduces your risk of being tracked.
Now, access is one thing; responsible behavior is another. Remember, legal and ethical behavior is paramount, no matter where you are online. Just because you have anonymity doesn’t mean you should engage in illegal activities. Here are some essential safety tips:
- Do not download anything from unknown sources. Be cautious of clicking on links, as they could be malicious.
- Use antivirus and anti-malware software. Keep your security software up-to-date.
- Be wary of scams. The anonymity on the Dark Web makes it a breeding ground for scam artists.
- Do not disclose personal information. Avoid any activity that might reveal your real identity, location, or personal details.
- Remember that law enforcement monitors the Dark Web. Be aware that online anonymity is never absolute.
- Stay updated on security threats. The Dark Web’s security landscape is continuously evolving, so it’s vital to stay informed.
Accessing the Dark Web is not an activity to be taken lightly. Curiosity is normal, but always prioritize safety.
4. Dark Web Search Engines and Tools: Finding Your Way in the Anonymous Depths
Once you’re on the Dark Web, it’s not as simple as typing a search term into Google. Standard search engines don’t index “.onion” sites, so you’ll need specialized tools. While not as user-friendly as Google, these Dark Web Search Engines help you navigate the anonymous web.
One of the most commonly used search tools, ironically, is DuckDuckGo. This privacy-focused search engine is also accessible on the Tor network. This is a good place to begin searches to find onion sites.
Other Dark Web specific search engines and directories include:
- Ahmia: A search engine that indexes .onion sites, though not all of them. It’s one of the more commonly used search tools on the Dark Web.
- Onion Links Directories: Various directories exist that list categorized .onion sites. These directories are often hosted on the Dark Web itself. Be aware that many of these are not actively maintained and could lead to malicious sites.
These Dark Web Search Engines differ greatly from traditional ones. The search algorithms are less sophisticated, making it harder to find what you need. The results can be highly variable, and not everything is safe for browsing.
Navigating the Dark Web is a bit like exploring a library without a card catalog. You need specialized tools and knowledge to find what you need, and you must be cautious of what you find.
5. Illegal Activities on the Dark Web: The Shadowy Side of Anonymity
While the Dark Web can serve legitimate purposes, it’s also notorious for its association with illegal activities. The very anonymity that allows journalists to communicate secretly also allows criminals to operate with a degree of impunity. Here’s a look at some of the most common illegal activities found on the Dark Web:
- Illegal Drug Markets: One of the most well-known uses of the Dark Web is the buying and selling of illicit drugs. This is one of the easiest to find, and often has reviews of vendors.
- Counterfeit Goods: Everything from fake IDs and passports to counterfeit money and consumer goods are commonly traded here.
- Stolen Data: Personal information, credit card details, and hacked databases are often bought and sold on the Dark Web.
- Weapons: Firearms and other dangerous weapons are illegally traded on some Dark Web marketplaces.
- Hacking Services: Some offer hacking services, tools, and malware on the Dark Web. This can include DDoS attacks, ransomware, and phishing toolkits.
- Human trafficking and exploitation: Unfortunately, the Dark Web facilitates criminal operations that harm vulnerable individuals.
It’s crucial to remember that engaging in any of these activities is dangerous and illegal. Law enforcement agencies actively monitor and combat cybercrime on the Dark Web. While you may feel hidden behind layers of encryption, sophisticated investigative tools and techniques are constantly being developed to track criminals operating in these dark spaces. Getting caught can result in severe legal repercussions.
The Dark Web is not just a place for curiosity; it’s a place where very dangerous and illegal activities take place daily. It’s essential to understand that even viewing illegal material on these sites can carry serious legal risk.
6. Dark Web Myths and Facts: Separating Fiction from Reality
Finally, let’s address some common misconceptions about the Dark Web. These Dark Web Myths and Facts will help you understand this mysterious part of the internet more accurately:
- Myth: “The Dark Web is 90% of the internet.”
Fact: The Dark Web is a tiny fraction of the internet. The Deep Web as a whole is far more expansive, encompassing private databases and other unindexed content. The Dark Web is merely a small subsection of this hidden content. - Myth: “The Dark Web is entirely illegal.”
Fact: While it has a strong association with criminal activity, the Dark Web also serves legitimate purposes such as privacy protection, secure communication, and freedom of information in censored regimes. - Myth: “You can’t be tracked on the Dark Web.”
Fact: While the anonymity tools used make it harder to track people, it is not impossible. Law enforcement agencies have developed tools and techniques to monitor and identify individuals operating on the Dark Web. Anonymity is never absolute online, even on the Dark Web. - Myth: “The Dark Web is some sort of spooky, different internet.”
Fact: It is still just the internet, but accessed using special software and employing methods to maintain privacy and anonymity. It operates on the same global infrastructure, and it isn’t some sort of alternate dimension. - Myth: “Everything is illegal on the Dark Web.”
Fact: While it’s home to many illegal activities, not every site is illegal or dangerous. There are forums for discussion, activism, and personal security. Just exercise caution to stay safe.
By debunking these myths, we can develop a more nuanced understanding of the Dark Web. It’s not simply a black-and-white issue; it’s a complex ecosystem with both good and bad elements.
Conclusion
The Dark Web is a complex and often misunderstood part of the internet. It’s not a place to wander aimlessly, but it’s crucial to understand its existence and purpose. From the anonymity it offers for journalists and activists to the illegal marketplaces it hosts, the Dark Web is a mirror of society, reflecting both the good and the bad.
Understanding the distinction between the Deep Web and the Dark Web, practicing safe access techniques, being aware of the risks, and challenging common misconceptions is the best way to stay safe and informed. The internet’s hidden corners hold many stories, but it’s essential to explore them with caution and awareness.
What’s your take on the Dark Web? Let us know below!

